Transfer Pricing Management Accounting Examples
Assume two units of a multinational corporation are located in two countries A and B. Length nature of prices or profits.

5 Transfer Pricing Methods Approaches Benefits Risks
Transfer pricing is the process methodology policy procedures of determining the price at which goods or services are exchanged internally between affiliates or divisions of an organization.

Transfer pricing management accounting examples. Example 1 suggested a transfer price between 18 and 80 but exactly where the transfer price is set in that range vastly alters the perceived profitability and performance of each division. In addition to encouraging division managers to focus on divisional profitability market-based transfer prices help to show the contribution of each division to overall company profit. Transfer pricing methods are ways of establishing arms length prices or profits from transactions between associated enterprises.
The higher the transfer price the better Division A looks and the worse Division B looks and vice versa. We will see that it could be the actual cost of the goods at the point of transfer their standard cost or a price above cost. There is no doubt that transfer pricing is an area that candidates find difficult.
One solution is to reduce the discretion of subunit managers in setting transfer prices. The application of transfer pricing methods. Tions of transfer prices namely the profit-allocation function reliable and trustworthy prices and thus reported profits and the coordination function guiding behavior of decentralized managers by using the trans-fer prices.
Management accounting courses teach that transfer prices are determined based on the selling divisions use of capacity. The profit of both companies will look like. The purpose of this article is to strip transfer pricing back to the basics and.
Again this general rule will depend on how much the seller has available. Assume that their income tax rate in country A is 40 and that in country B is 30. Ideally a transfer price provides incentives for segment managers to make decisions not only in their best interests but also in the interests of the entire company.
The basic guideline for setting price is the sellers differential cost plus its opportunity costs of not selling outside. That monetary value is the transfer price of the goods. Multinational firms set the transfer price taking into consideration the impact of the transfer price on direct and indirect taxes.
If a company within a multinational enterprise group MNE group provides an intra-group service to another company within that MNE group that company must charge an arms length fee for the service. Important to note transfer pricing does not affect the total organizational net income except for tax liabilities in multinational corporations but it affects individual business unit performance. After the management decides to do the transfer price they increase the selling price of ABC from 8 to 15 per unit.
For example if a subsidiary company sells goods or renders services to its holding company or a sister company the price charged is referred to as the transfer price. Let us take an example of income tax. Cost-Plus-Percent Method is an approach favored by some manufacturers and is popular with the aerospace industry.
A transfer price is based on market prices in charging another division subsidiary or holding company for services rendered. Transfer pricing is an accounting practice that represents the price that one division in a company charges another division for goods or services provided. The transaction between related enterprises for which an arms length price is to be established is referred to as the controlled transaction.
We can see that the tax expense has decreased from 39 to 25 per unit as the result of transfer pricing. For example say that a product has a transfer price of 15 and 100 items are transferred. For example applying 32 to your companys air travel costs would be insufficient 109 in the data but be too high for your rail travel costs 04 from the datainewscouknewsuk-inflation-rise-rates-increase-sharpest-record-food-transport-prices-1199915.
For example if the selling segment can sell everything it produces for 100 per unit the buying segment should pay the market price of 100 per unit. Entities under common control refer to those that are. Transfer prices based on market prices are consistent with the responsibility accounting concept of profit centres and investment centres.
Transfer pricing refers to the prices of goods and services that are exchanged between companies under common control. The accounting system will usually record the goods leaving one department and entering the next and some monetary value must be used to record this. Transfer pricing is the setting of the price for goods and services sold between controlled or related legal entities within an enterprise.
The total transfer price is 15 multiplied by 100 or 1500. Multiply the transfer price per item by the quantity of items transferred to arrive at the total transfer price. Its not surprising then that when it was examined in June 2014s Performance Management exam answers were not always very good.
Just like with any intra-group transaction the fee must be the same as what. For example if a subsidiary company. Prices fluctuate significantly for oil for example so for organizations that rely on oil for manufacturing this might not be the best transfer pricing model.
How to analyze intra-group services for transfer pricing purposes.
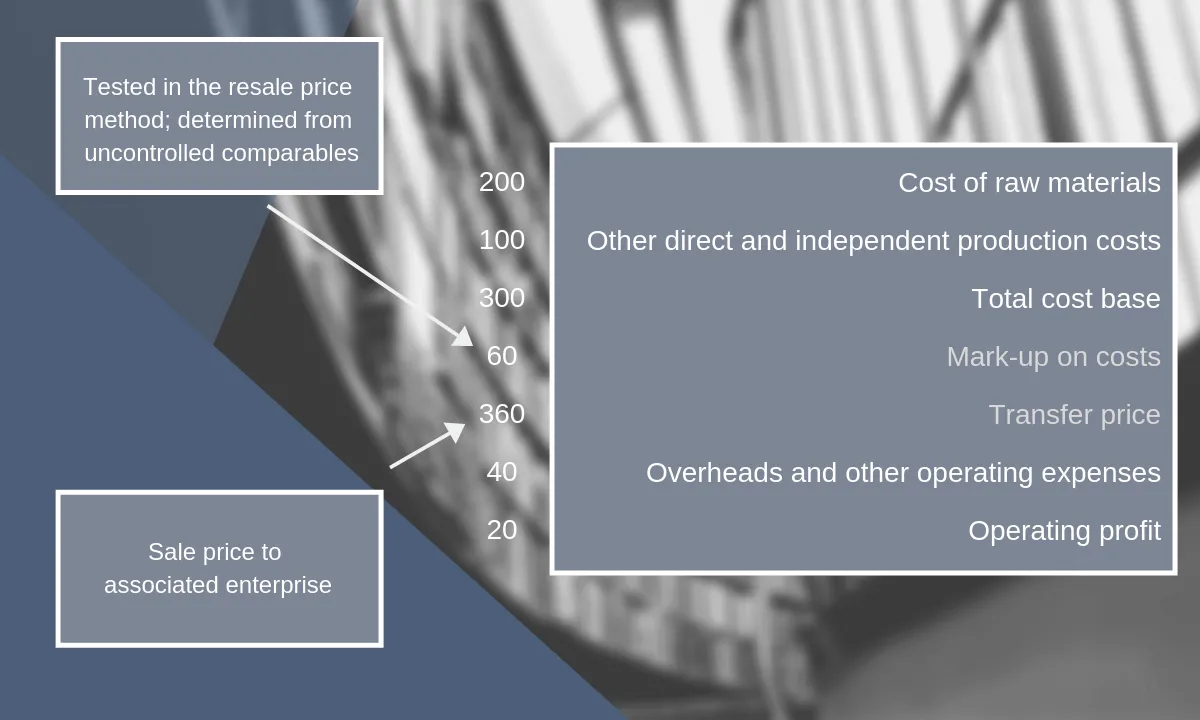
Transfer Pricing Methods Royaltyrange

The Cost Plus Method With Example Transfer Pricing Asia

The Five Transfer Pricing Methods Explained With Examples

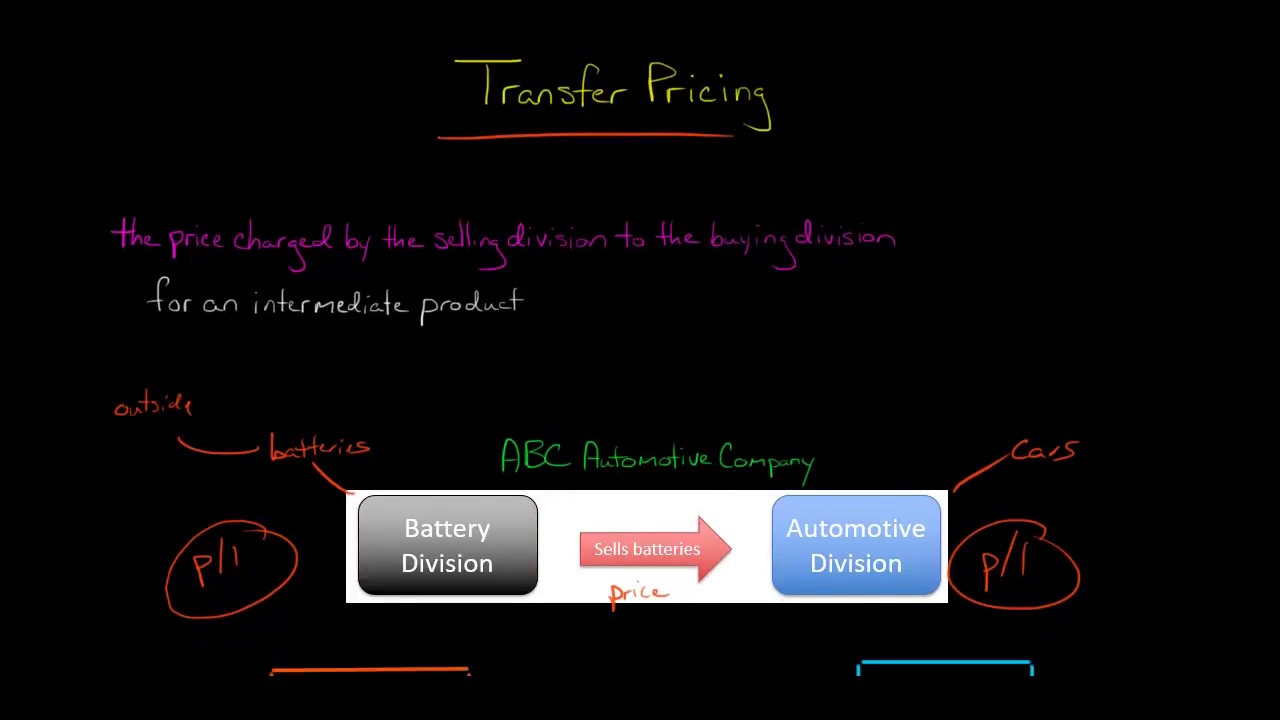
Transfer Pricing With Excess Capacity Youtube

The Cost Plus Transfer Pricing Method With Examples
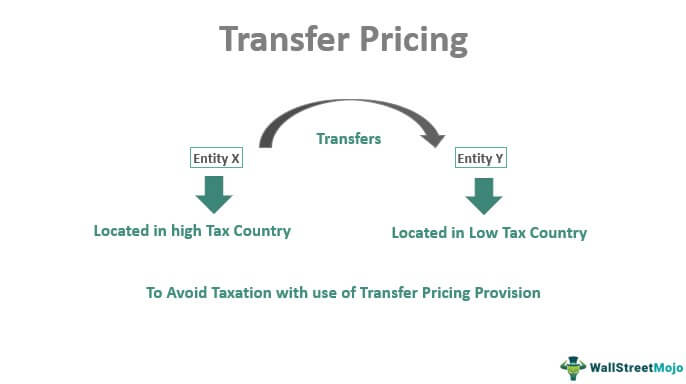
Transfer Pricing Meaning Examples Objectives Purpose

Pdf Transfer Pricing Practices Among Public Listed Companies Evidence From Malaysia

Transfer Pricing F5 Performance Management Acca Qualification Students Acca Global

The Five Transfer Pricing Methods Explained With Examples

The Five Transfer Pricing Methods Explained With Examples

Transfer Price Meaning Importance Example And More

The Five Transfer Pricing Methods Explained With Examples

Transfer Pricing And Its Effect On Financial Reporting
Posting Komentar untuk "Transfer Pricing Management Accounting Examples"